View this post on Medium.com
Send Data Across the Network with the <form> Element
Semantic HTML Basics
The HTML Form is a very important element in your job at a web developer. It is the primary tool that you'll have to send data from a web page to a server.
A very simple form might look like this
<form>
<input type="text" />
<button type="submit">submit</button>
</form>
The form element assumes that any buttons with type=submit, or no type assigned (because "submit" is the default type of a button :D ), will submit the form.
If you had ten buttons inside the form then each of them would trigger it.
<form>
<input type="text" />
<!-- all of these will cause form to submit -->
<button>submit</button>
<button>Sign Up Now</button>
<button>Leave a Review</button>
</form>
Action and Method
The most important attributes for the form are action and method.
The action is the location that you want to send your data. When the form is submitted, your web page will attempt to connect to that location on the internet with the information from the form.
The method is the HTTP "verb" (get or post) that you want to use with the form data. You will use a POST if you want to send the data in the form to a location over the internet. You will use a GET primarily for cases where submitting the form is actually redirecting the user back to your web page (generally for adding search filters to your page). For example
// to post data to an external endpoint
<form action="/my-data-endpoint/endpoint" method="POST">
<input type="text" />
<button type="submit">submit</button>
</form>
// for internal searches on your own page
<form action="/" method="GET">
<input type="text" />
<button type="submit">submit</button>
</form>
Other Attributes
Another important attribute is enctype, which specifies the content type that is contained in the form. If you are sending only text data you should use the default value, application/x-www-form-urlencoded. If you are sending files or images over the wire you need to use multipart/form-data.
Finally, you can specify the target of the form submission, in the same way that you can for a link. The common values here are _self (default): Load into the same browsing context as the current one. _blank: Load into a new unnamed browsing context.
Validation Using Forms
The form element contains everything you need for form validation through the <input> element. You can define validation rules on the input elements within the form. For example:
<form>
<input type="tel" pattern="[0-9]{10}" />
<button type="submit">submit</button>
</form>
The form will then be considered 'invalid' if the condition on that field are not met. You can do simple validation like minLength and maxlength as well as much more advanced validation using regular expressions https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Guide/Regular_Expressions.
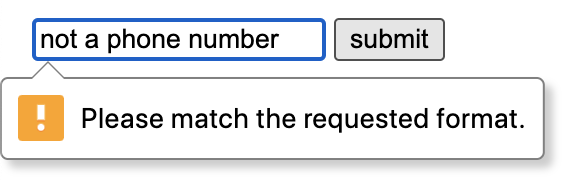
The default styles are very solid (seen above), but you can also use the :valid and :invalid CSS pseudo-classes to style a